From the department of cosmic justice comes this gem, spotted by researchers from Symantec: a trojan that targets
Windows,
Mac, and
Linux computers contains gaping security vulnerabilities that allow rival criminal gangs to commandeer the infected machines.
Known as Trojan.Jnanabot, or alternately as OSX/Koobface.A or trojan.osx.boonana.a, the bot made waves in October when researchers discovered its Java-based makeup allowed it to attack Mac and Linux machines, not just Windows PCs as is the case with most malware. Once installed, the trojan components are stored in an invisible folder and use strong encryption to keep communications private.
The bot can force its host to take instructions through internet relay chat, perform DDoS attacks, and post fraudulent messages to the victim's Facebook account, among other things.
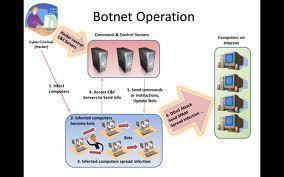
Now, Symantec researchers have uncovered weaknesses in the bot's peer-to-peer functionality that allow rival criminals to remotely steal or plant files on the victim's hard drive. That means the unknown gang that took the trouble to spread the infection in the first place risks having their botnet stolen from under their noses.
“Even though it's encrypted and even though it was written in
Java to make it cross-platform, it was still vulnerable to basically a directory transversal exploit,” Dean Turner, director of Symantec's Global Intelligence Network, said. “From a technical perspective, it goes to show that even if you have all those things where you're building in a secure platform, if you're not building application security into your malware, other bad guys will probably take advantage of it.”
Jnanabot's P2P feature is designed to make botnets harder to take down by providing multiple channels of communication. After sending an infected machine a single GET request, a website can discover all the information needed to upload any file to any location on the host's file system. Attackers can then install a simple backdoor on a user's machine by, for instance, writing a malicious program to a computer's startup directory.
Attackers can use the same vulnerability to steal files on infected machines.
Turner said the number of Jnanabot infections so far is “measured in the thousands,” rather than the hundreds of thousands for some of the
better-known trojans. Still, infection statistics gathered by Symantec in December are surprising. They show that about 16 per cent of infections hit Macs. They didn't show any infections on Linux machines. Turner said that Jnanabot attacks on the open source platform weren't able to survive a reboot.
Source: Symantec
The bot was discovered spreading over Facebook posts that planted the following message on infected users' Facebook pages: “As you are on my friends list I thought I would let you know I have decided to end my life.” An included link leads recipients to a cross-platform JAR, or Java Archive file that can run on Windows, Mac, or Linux. Once the recipient is infected, his Facebook page carries the same dire warning.
It's not the first time that malware developers have built gaping vulnerabilities into their wares. In September, researcher Billy Rios disclosed a weakness in the Zeus crimeware kit that makes it easy to take over huge networks of infected PCs.
Symantec has more about the trojan
here,
here, and
here.